Medical Mystery Uncovers New Host for Rat Lungworm Parasite

The rat lungworm parasite, scientifically known as Angiostrongylus cantonensis, has long been recognized for its impact on human health. This parasitic nematode is notorious for causing eosinophilic meningitis, a serious condition that can lead to severe neurological symptoms. Recently, a medical mystery has unfolded with the discovery of a new host for the rat lungworm parasite. Understanding and identifying new hosts are crucial in preventing the spread of this disease and protecting public health.
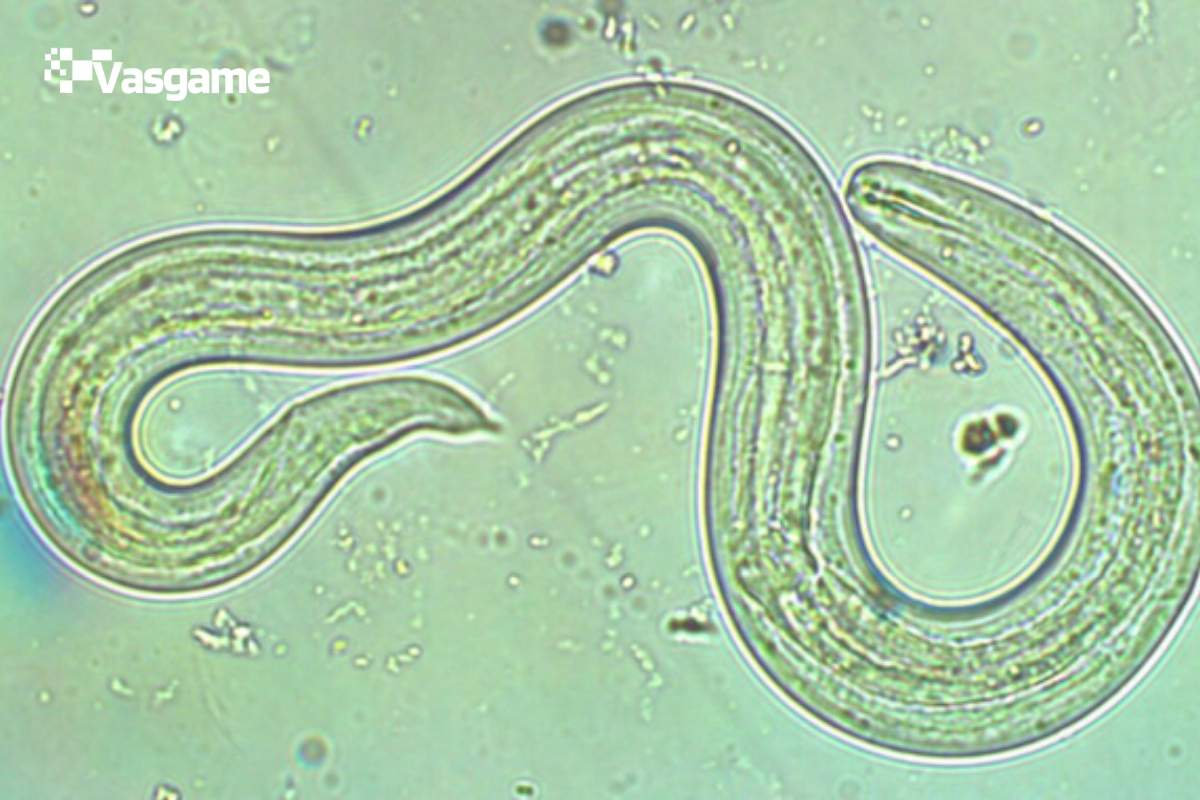
What is the Rat Lungworm Parasite?
Scientific Name: Angiostrongylus cantonensis
The rat lungworm parasite, Angiostrongylus cantonensis, is a parasitic nematode primarily found in rats. Its lifecycle is complex and involves multiple hosts.
Lifecycle of the Rat Lungworm Parasite
- Primary Hosts: Rats are the definitive hosts where the adult parasites reside in the pulmonary arteries.
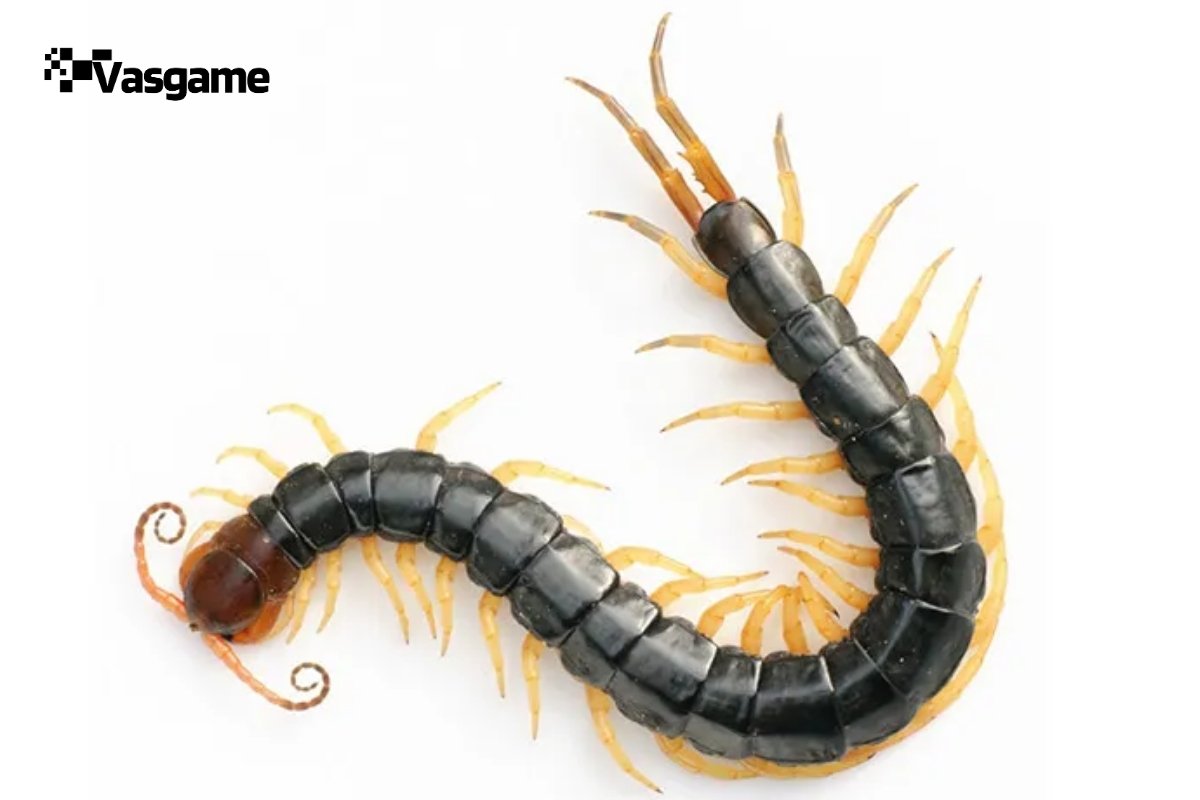
- Intermediate Hosts: The parasite’s larvae are commonly found in snails, centipedes and slugs, which serve as intermediate hosts. These larvae develop within the mollusks before becoming infective.
- Accidental Hosts: Humans and other animals can become accidental hosts when they consume contaminated food, water, or inadvertently ingest infected intermediate hosts.

Transmission to Humans
Human infection typically occurs through the consumption of raw or undercooked produce that is contaminated with the larvae, or by drinking contaminated water. Accidental ingestion of infected snails or slugs can also lead to infection.
Health Effects of the Rat Lungworm Parasite
- Eosinophilic Meningitis: The most severe health impact is eosinophilic meningitis, which can cause headaches, nausea, vomiting, neck stiffness, and even paralysis.
- Reported Cases: Cases of rat lungworm infection have been reported in Hawaii, the southern United States, and Southeast Asia, indicating a widespread geographical presence.
The Medical Mystery – A New Host Discovered
Background of the Discovery
Scientists began noticing unusual cases of rat lungworm infection in regions where common intermediate hosts, like snails and slugs, were not present. Patients exhibited symptoms indicative of rat lungworm exposure but had no known contact with the traditional carriers of the parasite.
Investigation Process
- Wildlife Surveillance and Laboratory Testing: Researchers conducted extensive wildlife surveillance and laboratory testing to identify the source of these infections.
- Genetic Analysis: Genetic analysis played a pivotal role in confirming the presence of the rat lungworm parasite in a new host species.
